Helium Element
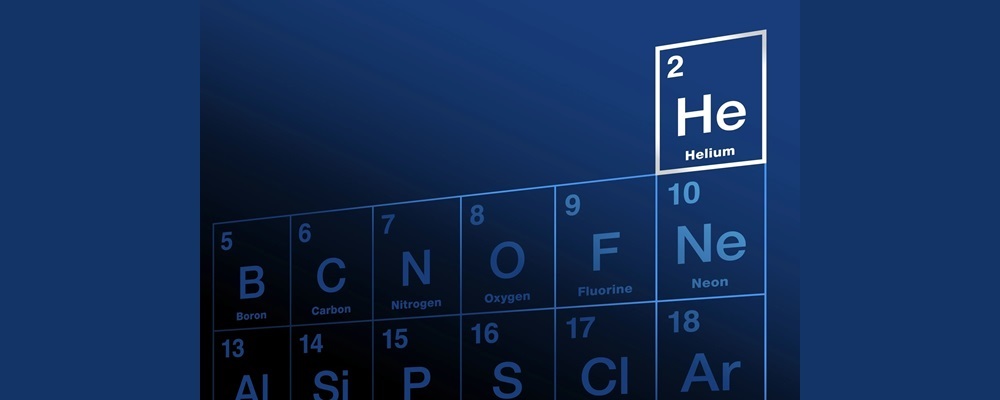
Helium is a chemical element located in period 1 and group 18 (also known as the noble gas group) of the periodic table. It has atomic number 2 and symbol He. Helium is the second most abundant element in nature after hydrogen, but its presence is very limited in Earth's atmosphere.
Following are some of the main characteristics of helium:
Inert Gas
Helium is a noble or inert gas, meaning it tends not to react chemically with other elements because it has a completely filled electron shell configuration. Because of this property, helium is considered very chemically stable.
Non-Reactive
Because it belongs to the noble gas group, helium does not readily react with other elements to form chemical compounds. This makes helium useful in a variety of applications where an inert gas is required.
Light and Colorless
Helium is a very light, colorless gas. These properties make it useful as a filling gas for hot air balloons and as an inert gas in various industrial processes.
Low Boiling Point
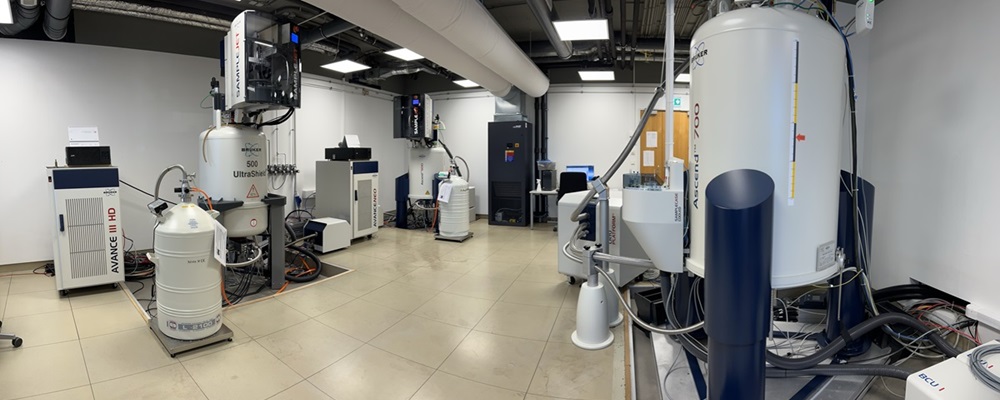
One of helium's unique properties is its extremely low boiling point, around -268.93 degrees Celsius. This makes helium useful in cryogenic applications, such as cooling for low-temperature physics research or as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology.
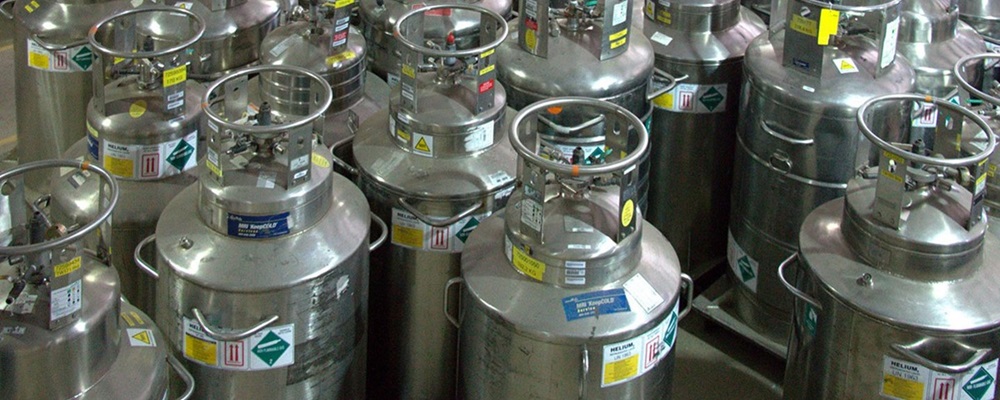
Availability
Helium is found naturally as a byproduct of natural gas extraction. However, Earth's helium reserves are not rapidly replenished because it cannot be produced naturally in significant quantities. Therefore, the wise and efficient use of helium is crucial.
Application
Helium has a wide range of applications, including as a filling gas in hot air balloons, in the oil and gas refining industry, in superconductor cooling, in space technology, and in scientific research in various fields.
Helium has unique and useful properties, making it a vital element in a wide range of industries and modern technologies. Due to its limited availability in nature, continued attention is paid to managing its use efficiently and ensuring its future availability.