NMR Machine
A Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) machine is a laboratory device used to perform NMR spectroscopy. It is an essential tool in various scientific fields, including chemistry, biology, physics, medicine, and materials science. NMR machines work on the principle of magnetic resonance of atomic nuclei in a sample placed within a magnetic field.
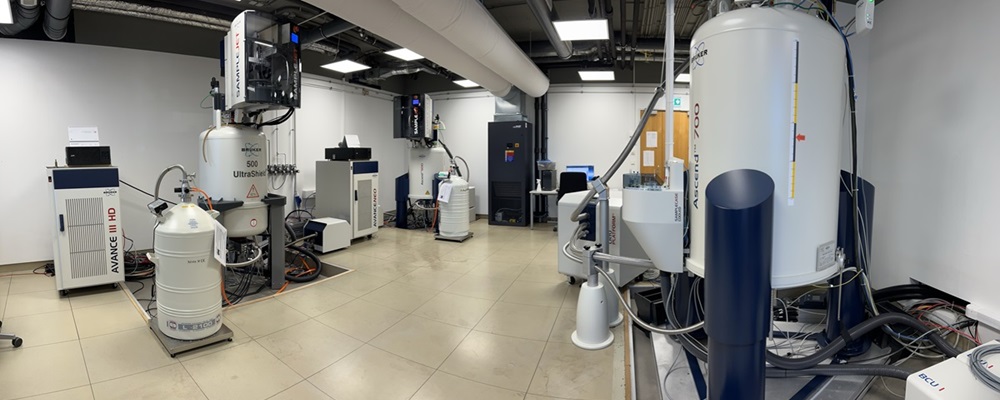

Following are some of the main components of an NMR machine:
Magnet
NMR machines are equipped with superconducting magnets that generate extremely strong magnetic fields. These magnetic fields are essential for orienting atomic nuclei in a sample into measurable magnetic resonances.
NMR probe
An NMR probe is a component that contains the sample to be analyzed. It typically consists of an RF coil (radiofrequency coil) to deliver RF pulses to the sample and detect the resulting NMR signals.
RF Pulse Sender
An NMR machine is equipped with an RF pulse transmitter that generates radiofrequency pulses at specific frequencies. These RF pulses are used to change the spin orientation of atomic nuclei in a sample, a crucial step in an NMR experiment.
NMR Signal Receiver
After the sample undergoes magnetic resonance and emits NMR signals, an NMR receiver (often the same RF coil as the probe) detects these signals. These signals are then amplified and processed to produce an NMR spectrum that can be analyzed.
Electronic Control and Software
NMR machines are equipped with electronic controls and computer software that regulate and control the entire experimental process. This software is also used to process NMR spectral data and analyze the results.
Cooling System
NMR machines often require a cooling system to keep the superconducting magnets at the low temperatures necessary to remain in the superconducting state.
NMR machines are used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Identification and characterization of chemical compounds in samples.
- Understanding of molecular structure and molecular interactions.
- Qualitative and quantitative analysis of components in a mixture.
- Monitoring of chemical reactions and molecular dynamics.
- Study of the properties of materials, including cryogenic materials, superconductors, and others.
NMR machines are very important tools in research and practical applications in various fields of science, because of their ability to provide in-depth information about the structure and properties of matter at the molecular level.